Allergy Testing & Treatment
Millions of people suffer from nasal allergies. The most appropriate person to evaluate nasal allergy and sinus symptoms is our physician, the Otolaryngologist (ear, nose and throat physician).
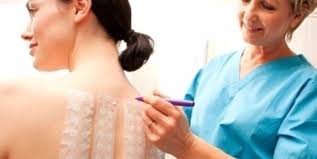
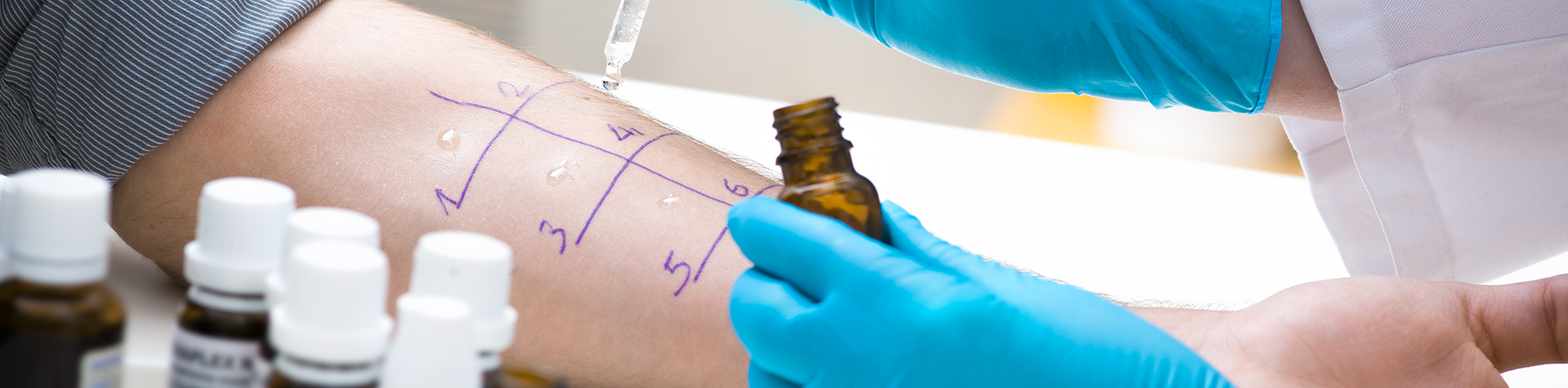
We treat both adults and children. Our skin testing is done mainly on the upper arm, and involves placing a small amount of antigen under the first layer of skin, creating a “wheal”. The wheal is timed for ten minutes and then measured. We test for 34 antigens routinely.
Patients may need more intra-dermal wheals depending on the extent of the allergic disease. We offer a numbing cream that can be applied one hour before the testing appointment to help alleviate any discomfort associated with the skin testing.
The physicians and clinicians at North Atlanta Sinus and Sleep Center make patient care our #1 concern. Our goal is to make the patient experience as pleasant as possible and address the needed symptom relief. We encourage patients who have questions concerning allergy testing and treatment to please contact our office, and our experienced allergy technician will address the question or concern.
Inhalants and Allergic Rhinitis
Allergies, or allergic rhinitis, is a disorder that occurs when the body detects foreign substances called allergens (triggers). Allergies occur because the body’s defense system mistakes harmless allergens for something potentially harmful (such as bacteria).
The symptoms of allergic rhinitis occur when a substance called histamine is released into the blood. The histamine causes the most common symptoms of allergies, such as sneezing, itchy and watery eyes, runny nose, itchy throat and a stuffy nose. Other less common symptoms a patient might experience include chronic sinusitis, dizziness, ear problems, rashes, hives and stomach problems.

We are able to test and treat a variety of allergy-related disease processes, such as indoor and outdoor inhalants, stinging insects, and food and fungus allergies.
Utilizing three techniques to manage allergies, the patient will receive the maximum relief of their symptoms:
Avoidance
The first line of therapy for allergies is avoidance. Knowing what activates allergies through allergy testing allows allergy sufferers to avoid being exposed to harmful triggers.
Medication
Medications such as antihistamines, nasal sprays, steroids and decongestants may provide temporary relief, but do not address the underlying immune problem.
Food Allergy
One study found that 60% of the general population exhibited symptoms of food allergy. Of this number, 10% were severe enough to require medical treatment.
Food allergy is a progressive disease that builds on itself. An allergic individual becomes progressively worse until their symptoms become severe enough to seek medical treatment.
If you are born with the tendency to develop a food allergy, it will be to the foods that you “repeat” eat, meaning foods you are eating every day. In our society of processed foods, we are eating hidden ingredients, such as milk, soy, wheat or corn on a daily basis.

There are two types of food allergies:
Food allergy treatment is a combination of avoidance and rotation diet. There are treatment options available that can be discussed once skin tested has been completed.
Fungal Allergy
Fungus lives on our skin naturally. A break in the skin can allow the fungus to enter the body, resulting in an infection. This infection can cause a variety of symptoms, including rashes and gastrointestinal problems. Common sites for fungal infections are: nails, skin (including scalp and groin area), ear canal, vagina and the gastrointestinal tract. Treatment options are diet to eliminate foods that “feed” the fungus and immunotherapy. Immunotherapy desensitizes the body from the fungus.
Stinging Insect
Stinging insect allergy is an allergic reaction to a bee sting. The reaction can be mild, resulting in localized redness and swelling at the sting site. Reactions can become severe enough to cause anaphylactic shock. Anaphylactic shock is a sudden, severe and potentially fatal allergic reaction. It is marked by a drop in blood pressure, itching, swelling and difficulty breathing.






 Make an Appointment
Make an Appointment